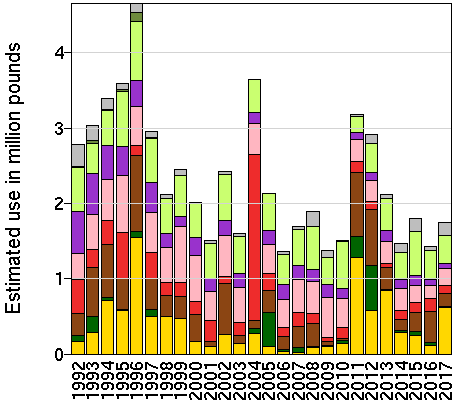Dimethoate
dee-meth-oh-ayt
High residues found on frozen strawberries, frozen spinach, and other foods. Registered as a U.S. pesticide in 1972. Reregistered in 2006. Currently under registration review.
Overview
Dimethoate is used in 28 states.
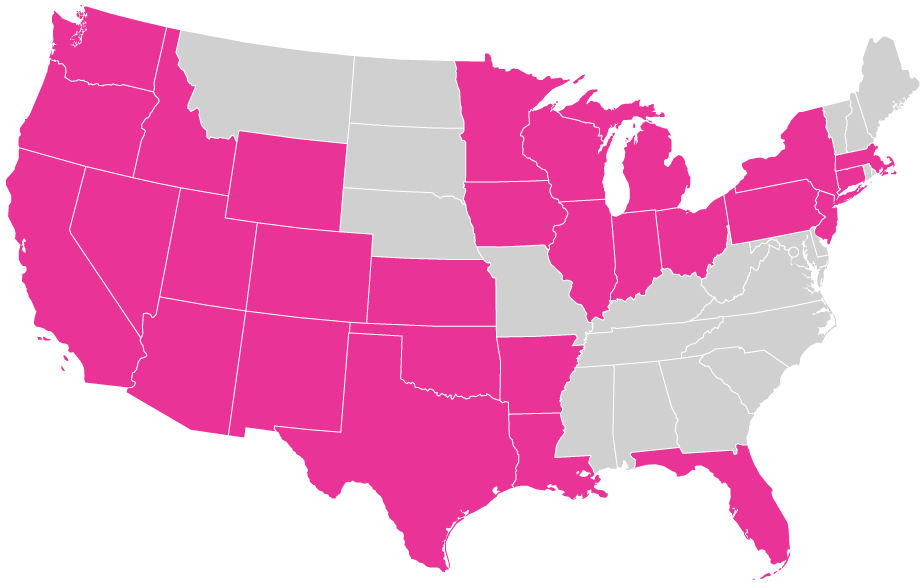
Dimethoate is used in Arizona, Arkansas, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Florida, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Louisiana, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Nevada, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Texas, Utah, Washington, Wisconsin, and Wyoming.
Data is not available for Alaska, D.C., Hawaiʻi, and U.S. Territories. Data represents the most recent year available from USGS. Details.
See detailed maps of dimethoate usage by state and county.
Human Health Effects
Even at low levels of exposure, dimethoate can lead to serious negative health effects.
Cancer
Endocrine Disruption
Neurodevelopmental Harm
Reproductive Toxicity
High Risk Exposure Routes
People are exposed to dimethoate through food and drinking water, even if they don’t live near areas where pesticides are sprayed. Details.
Food and/or Drinking Water
FarmworkersPeople performing post-application activities in previously treated fields, but do not directly apply pesticides themselves. Details.
Pesticide HandlersPeople involved in pesticide application process. Details.
Residential BystanderPeople who live near areas where pesticides are applied. Details.
Spray Drift
High Residue Foods
Where residue levels of dimethoate exceeded allowable limits or were not legally allowed to have residues.Details.
Basil
Cilantro
Mangoes
Frozen Spinach
Frozen Strawberries
Snap Peas
Percentage of Crops
Dimethoate is applied on food widely grown and consumed in the United States.
Broccoli (55%)
Cauliflower (45%)
Tomatoes (40%)
Celery (35%)
Lettuce (35%)
Green Peas (25%)
Oranges (25%)
Peppers (25%)
Registered Uses
Where EPA allows dimethoate to be used.
Agricultural Crops: alfalfa, corn, cotton, fruit and vegetables, orchards and grapes, wheat, other crops
Christmas Tree Farms
Ornamentals in Outdoor Nurseries
Trees Grown for Pulp
Additional Information
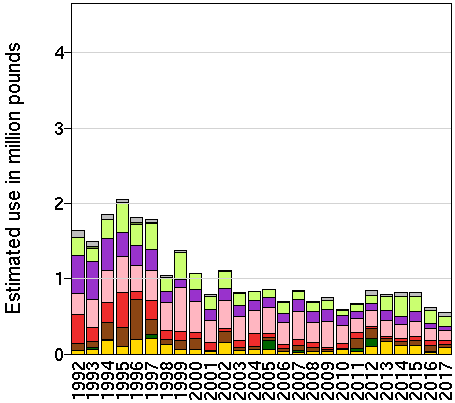
Estimated Use of Dimethoate on Crops
Most recent agricultural crop usage data as provided by the U.S. Geographical Survey’s Pesticide National Synthesis Project. Does not reflect universal usage of dimethoate. (How do EPest-low and EPest-high differ?)
U.S. Tolerances Categories & Commodities for Dimethoate
The U.S. EPA sets maximum residue limits — known as “tolerances” — on the amount of dimethoate that may remain in and on foods. The tolerance is the residue level that triggers enforcement actions.
Tolerances have been set for dimethoate for: Agricultural Commodities and Milk Eggs Meat and/or Poultry. Maximum residue limits have been set for dimethoate by the U.S. EPA for the following commodities:
Asparagus
Beans
Blueberry
Broccoli
Brussel Sprouts
Cattle
Cauliflower
Cherry
Citrus
Corn
Cotton
Egg
Endive
Goat
Hog
Kale
Lemon
Lettuce
Melon
Milk
Mustard Greens
Pea
Pear
Pecan
Pepper
Potato
Poultry
Safflower
Sorghum
Soybean
Swiss chard
Tangerine
Tomato
Turnip
Wheat
U.S. EPA Human Health Risk Assessments for Dimethoate
Human Health Risk Assessments are conducted by the U.S. EPA to estimate the nature and probability of harmful health effects in people who may be exposed to pesticide. They are used to make informed decisions about approving new pesticides and new uses of registered pesticides, and during our regular review of existing pesticides. Read the assessment for dimethoate.